Simple failover cluster using UCARP on Ubuntu
In this tutorial, I’ll show you the steps to create a simple failover cluster on Ubuntu using CARP. To make the things meaningful,we’ll create the cluster for Apache service but you can use it for any other service, which relay on IP.
Scenario:
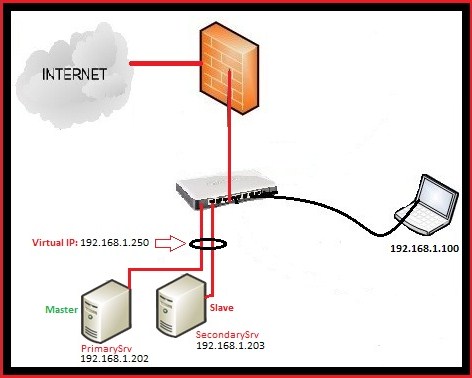
Here is my Setup:
PrimarySrv: This is the main server, where I configured the apache and which act as Master (IP: 192.168.1.202)
SecondarySrv: 2nd Apache Server where I configured the apache exactly like on PrimarySrv (IP : 192.168.1.203)
192.168.1.250 : Virtual IP address,created using Ucarp.
Ucarp is really simple, it works like this,when the PrimarySrv is up,it will assign the virtual IP 192.168.1.250 to it, in case that PrimarySrv is down then it will assign virtual IP to the SeconadrySrv and when the PrimarySrv will come online, it will assign the virtual IP once again to it.